The patient

Patient right profile
Bilateral ectasia post myopic lasik by eye rubbing
Identity : Ms P.E
First visit : 01/05/2017
Last Visit : 03/27/2018
Ms. P.E is a 39-year-old female who had bilateral LASIK in 2009 performed in another institution. During the postoperative course, she suffered from chronic dry eye. She subsequently complained of a reduction of vision which was more pronounced in the right eye, with progressive deterioration noticed two years .
Her refraction at the first visit (January 5th, 2017) was : Right Eye (RE) 20/20 with -0.25 (-3 x 45 °) and Left Eye (LE) 20/20 with +0.25 (-1.75 x 145 °).
Clinical examination with the slit lamp revealed thin corneas. The edge of the LASIK flaps could be delineated.
Corneal topography revealed the presence of bilateral corneal ectasia post LASIK, more pronounced in the right eye.
When asked about the possibility of abnormal eye rubbing, the patient admitted that she had rubbed her eyes regularly following the surgery, to soothe her constantly irritated eyes. She did not remember rubbing her eyes before the LASIK.
We strongly counselled and encouraged her to stop rubbing her eyes. We gave this patient an appointment for a review visit, which was scheduled several months later.
Here are pictures of the patient rubbing her eyes and her profiles
 PATIENT RIGHT EYE PROFILE
PATIENT RIGHT EYE PROFILE PATIENT LEFT EYE PROFILE
PATIENT LEFT EYE PROFILE PATIENT SHOWING HOW SHE RUBS HER EYES. She uses her index finger to massage the globes laterally and vertically.
PATIENT SHOWING HOW SHE RUBS HER EYES. She uses her index finger to massage the globes laterally and vertically. PATIENT SHOWING HER UNHEALTHY SLEEPING POSITION (ON THE RIGHT SIDE). This position may induce chronic irritation and inflammation in the right eye, which causes additional pruritus.
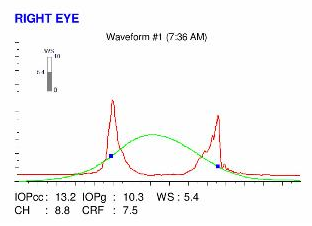
PATIENT SHOWING HER UNHEALTHY SLEEPING POSITION (ON THE RIGHT SIDE). This position may induce chronic irritation and inflammation in the right eye, which causes additional pruritus.Here are the Orbscan quadmaps, Pentacam maps, OPDscan (topography and aberrometry) maps, Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA) and OCT results obtained during the first visit .
Difference maps were performed at each subsequent visit. No evolution was observed between the first and last visits. The corneal ectasia is stable, more than 14 months after the patient had definitively stopped rubbing her eyes .
The induced corneal ectasia (or iatrogenic keratoconus) is a rare complication of LASIK that compromises vision.
The role of eye rubbing in post LASIK ectasia is probably underestimated. It should be suspected for every case of ectasia, especially in late onset post-LASIK ectasia. Abnormal eye rubbing is triggered by ocular dryness as a consequence of LASIK. Since the cornea is thinned by the LASIK procedure, it makes the corneal wall more vulnerable to eye rubbing. It is mandatory to explain to LASIK patients that they should avoid excessive eye rubbing after the surgery. In our experience, the cessation of eye rubbing permits stabilisation of the corneal deformation in post-LASIK ectasia, as in primary keratoconus.