Patient left profile
Case #67
The patient

Unilateral corneal ectasia post lasik induced by eye rubbing
Identity : Ms W.W
First visit : 07/11/2017
Last Visit : 12/12/2017
Ms. W.W is a 50-year-old female who had bilateral LASIK performed in 1999 for myopia (- 3 D). She was referred to us by an ophthalmologist to evaluate the increasing astigmatism in her left eye since 2014, which was causing a progressive decrease in visual acuity. She had already sought an opinion in another institution, where she was advised to have corneal collagen cross-linking on an urgent basis.
Her refraction at the first visit at the Rothschild Foundation (on 07/11th/2017) was: Right Eye (RE) 20/20 with -1 (-0.5 x 35 °) and Left Eye (LE) 20/25 with -0.75 (-3.75 x 115 °).
Clinical examination with the slit lamp suggested a thin and irregular left cornea. We also found bilateral tarsal papillae (more pronounced in the left eye), and signs of dry eye.
Corneal topography performed at our institution revealed the presence of unilateral post LASIK ectasia in the left eye.
At the first visit, when asked about the possibility of frequent eye rubbing, the patient admitted to rubbing her eyes when she awoke in the mornings and after removing her eye makeup.
With regards to her sleeping habits, she described sleeping on her left side or stomach, with the head buried in the pillow (pillow hugging). She is allergic to dust mites, and shared how her left eye was more often irritated than the right one.
We explained to the patient that since vigorous rubbing had preceded the drop in visual acuity, this habit may have caused the cornea to deform, leading to the classic clinical presentation of corneal ectasia in her case.
We strongly advised this patient to stop rubbing her eyes and to change her unhealthy sleeping position.
At the subsequent visits, the patient informed us that after being primed about the deleterious effects of eye rubbing, she had come to realize that she was rubbing her eyes more often than she had thought initially. She has also since tried her best to alter her sleeping posture.
Here are pictures of the patient rubbing his eyes and his profiles
 PATIENT RIGHT PROFILE. The corneal profile is noticeably flatter than that of the left eye.
PATIENT RIGHT PROFILE. The corneal profile is noticeably flatter than that of the left eye. PATIENT LEFT PROFILE.
PATIENT LEFT PROFILE.  PATIENT RUBBING HER EYE WITH HER KNUCKLES. When asked to demonstrate her eye rubbing technique, the patient spontaneously rubbed her left eye with the knuckle of her left index finger, despite being right handed.
PATIENT RUBBING HER EYE WITH HER KNUCKLES. When asked to demonstrate her eye rubbing technique, the patient spontaneously rubbed her left eye with the knuckle of her left index finger, despite being right handed. PATIENT DEMONSTRATING HER SLEEPING POSITION (LEFT SIDE). The patient sleeps on her left side with her left eye buried in the pillow.
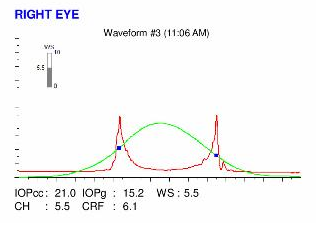
PATIENT DEMONSTRATING HER SLEEPING POSITION (LEFT SIDE). The patient sleeps on her left side with her left eye buried in the pillow. Here are the Orbscan quadmaps, Pentacam maps, OPD scans, Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA) results, Corneal Cross-sectional OCT and epithelial maps of the first visit. Unfortunately, no pre-LASIK topographies or other examinations are available.
Difference maps were performed at each subsequent visit. No evolution was observed between the first and last visits. The corneal ectasia is stable, more than 5 months after the patient definitively stopped rubbing her eyes .
In this case we find many triggers for eye rubbing like eye rubbing and an unhealthy sleeping position. The unilateral or asymmetric nature of corneal ectasia development may be related to the sleeping position (left sided) and the habit of preferentially rubbing the left eye.
Other cases :
- Date 14 janvier 2018
- Tags Allergy, Asymmetric, Cross linking, Dry eyes, Ectasia, Eye rubbing, Female, Fleischer ring, Knuckles rubbing, Lasik, Morning rubbing, Oldest, Pillow hugging, Removing makeup rubbing, Sleep position